Why database on Kubernetes ?
TLDR
Want a quick introduction check this excellent video from my colleague Michael Cade.

Having your database in Kubernetes has several advantages :
- Performance : you colocalize the data and the application
- Security : All stay within the kubernetes network
- Ease of deployment :
kubectl apply -f ...and you’re good to go. - Automation : You define your desired state, the operator make it happen.
- Self Healing : Benefits for all workloads in Kubernetes.
However there are challenges :
- Enterprise scale : HA and big volumes are required.
- Efficient Protection : Incremental backup, transaction consistency.
- Ease of use : GUI and easy to use API.
- Skill shortage : Database and kubernetes double skills are hard to find.
- Migration and replication : we are more than ever in a hybrid momentum.
Especially the last one Migration and replication : no serious player would want to get trapped with a single cloud provider. How can you negotiate your bill without the flexibility to move? How can you adapt to legal compliance changes? How do you move and replicate accross the cloud and the datacenters ?
EDB and Kasten together can overcome all these challenges let’s see how.
How EDB and Kasten work together ?
EDB on Kubernetes
EDB offer a full management of postgres clusters on Kubernetes. The only thing you have to do is create a custom resource like this one :
apiVersion: postgresql.k8s.enterprisedb.io/v1
kind: Cluster
metadata:
name: cluster-example
annotations:
"k8s.enterprisedb.io/addons": '["kasten"]'
spec:
instances: 3
storage:
size: 1Gi
“Et Voila”, you immediately get a postgres cluster with one primary and 2 replicas. If the primary becomes unavailable, the operator immediately handles the failover to one of the replicas and promotes it to primary. In addition to the failover, the operator automatically adds a new replica to bring the database to a desired state. All that automatically.
EDB is the company behind the very well known Open Source Kubernetes project CloudNativePG, and you can get support and professional services from EDB through their commercial offering. You can see an EDB database as a managed database but without being tied in a cloud provider or a data center.
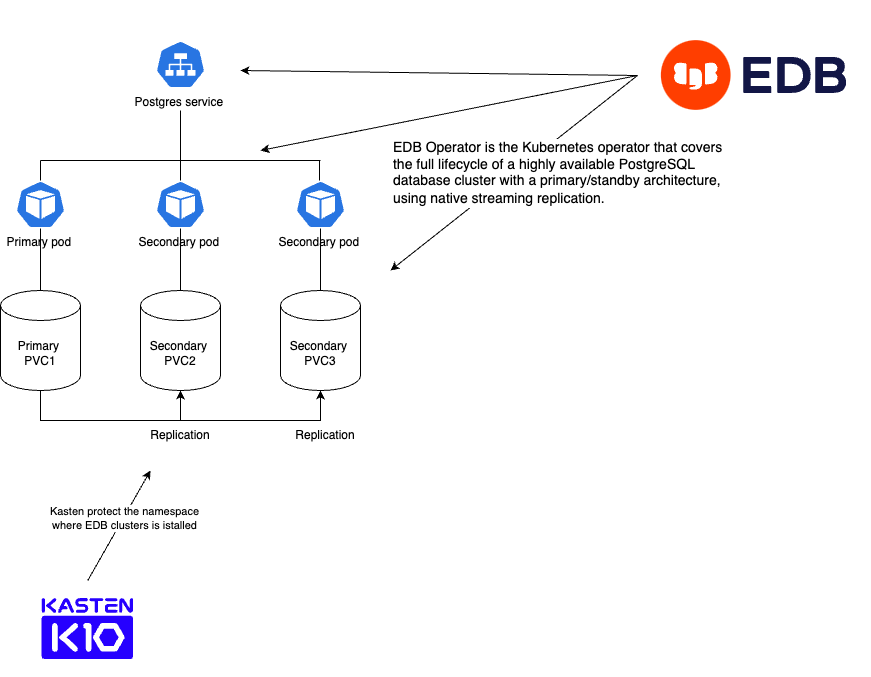
Solution
In it’s regular run EDB manages the postgres cluster ensuring there is always one primary (read-write) and 2 replicas (read-only) to handle failover scenarios.
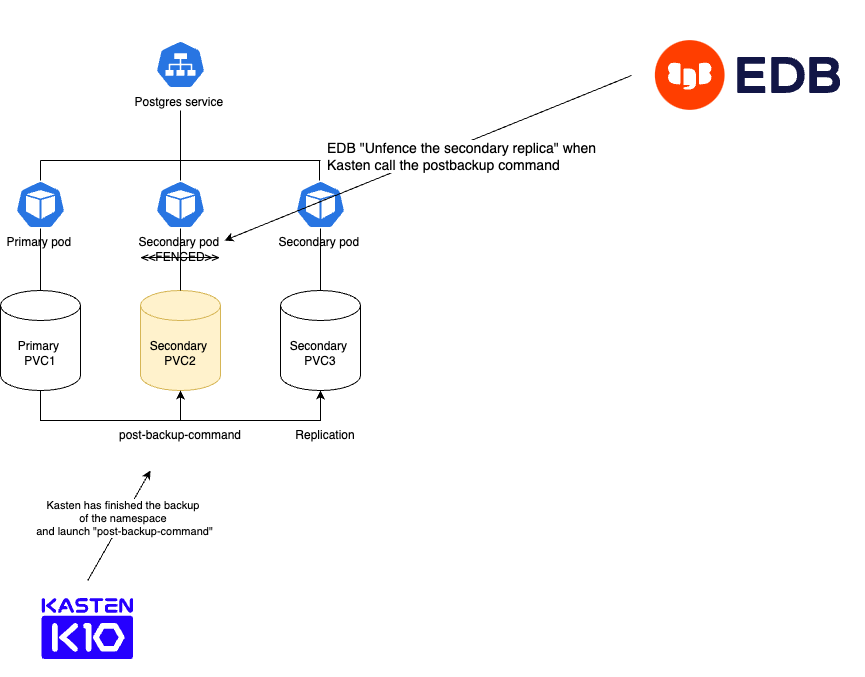
When Kasten launch the backup it calls the command to “Fence” one of the replica. It means that the primary instance is not affected and all the transactions can continue on the primary. Customer won’t notice any downtime or performance drop because of the backup !
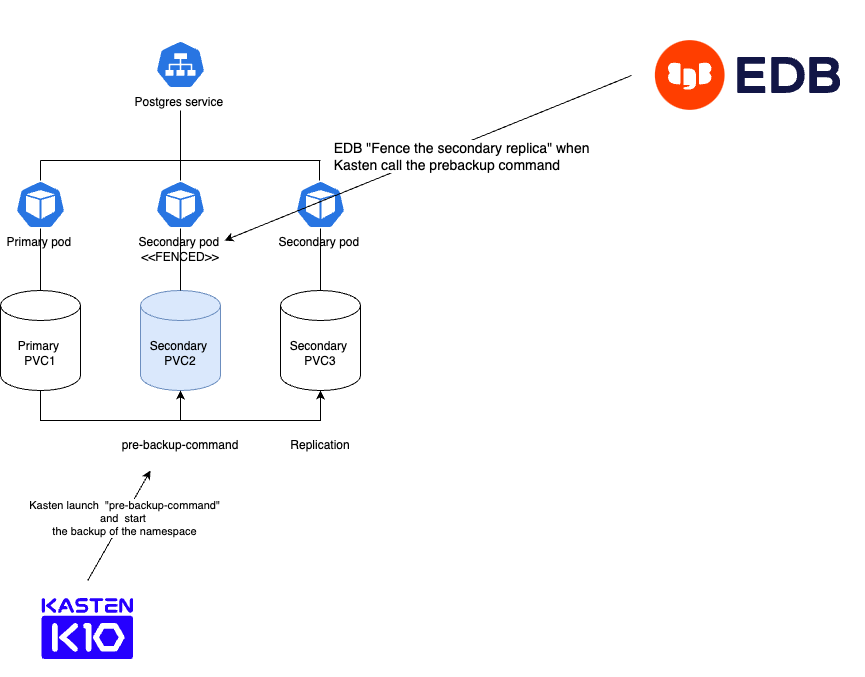
When an instance is “fenced” , EDB guarantees consistency by committing all transactions to the database. This ensures that the backups taken by Kasten is a full consistent snapshot of the database.
When the snapshot of the “fenced” instance is complete, Kasten will “unfence” and the replica catches up with the last transaction that was missed during the fencing.
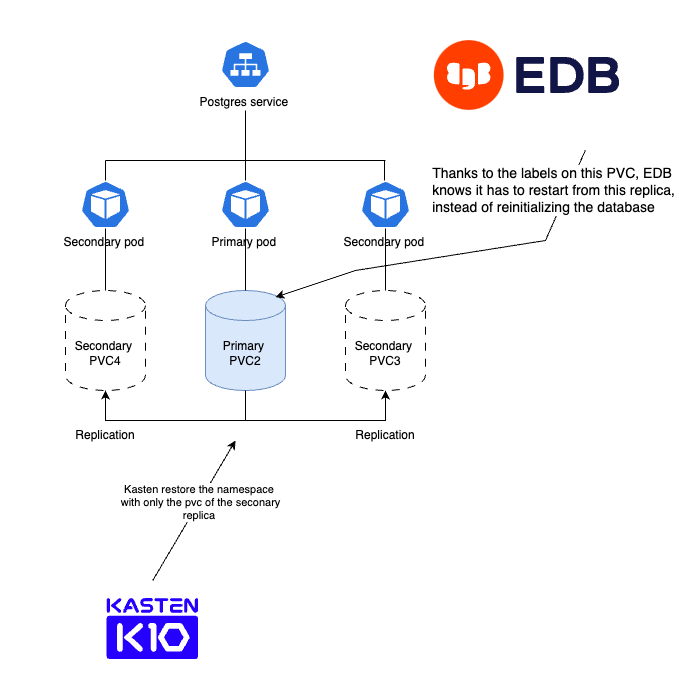
During restore, Kasten restores the PVC that was fenced, and when complete the operator promotes it as a primary instance. Two read replicas are then created from the primary.
Let’s try it now
Install the operator
If you already have EDB operator installed on kubernetes you can skip this part
kubectl apply -f https://get.enterprisedb.io/cnp/postgresql-operator-1.20.2.yaml
This will create the operator namespace where the controller will be running.
Create an EDB cluster, a client and some data
kubectl create ns edb
kubectl apply -f https://github.com/michaelcourcy/edb-kasten/raw/main/cluster-example-2.yaml -n edb
Wait for the cluster to be fully ready.
kubectl get clusters.postgresql.k8s.enterprisedb.io -n edb
NAME AGE INSTANCES READY STATUS PRIMARY
cluster-example 19m 3 3 Cluster in healthy state cluster-example-1
Install the cnp plugin if you haven’t it yet
curl -sSfL \
https://github.com/EnterpriseDB/kubectl-cnp/raw/main/install.sh | \
sudo sh -s -- -b /usr/local/bin
Create a client certificate to the database
kubectl cnp certificate cluster-app \
--cnp-cluster cluster-example \
--cnp-user app \
-n edb
Now you can create the client
kubectl create -f https://github.com/michaelcourcy/edb-kasten/raw/main/client.yaml -n edb
Create some data
kubectl exec -it deploy/cert-test -- bash
psql " $DATABASE_URL "
\c app
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS links;
CREATE TABLE links (
id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
url VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL,
name VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL,
description VARCHAR (255),
last_update DATE
);
INSERT INTO links (url, name, description, last_update) VALUES('https://kasten.io','Kasten','Backup on kubernetes',NOW());
select * from links;
\q
exit
Add the backup decorator annotations to the cluster
Skip this step if you have created the cluster using the instructions from the previous section. With cluster-example-2 the yaml includes the kasten addon.
If you haven’t used the instructions from the previous section, add this annotation to your cluster CR
"k8s.enterprisedb.io/addons": '["kasten"]'
If your version of EDB is old and does not support the kasten addons you can create all the annotations and labels manually using the example in cluster-example.yaml .
Install the edb blueprint
kubectl create -f https://github.com/michaelcourcy/edb-kasten/raw/main/edb-hooks.yaml
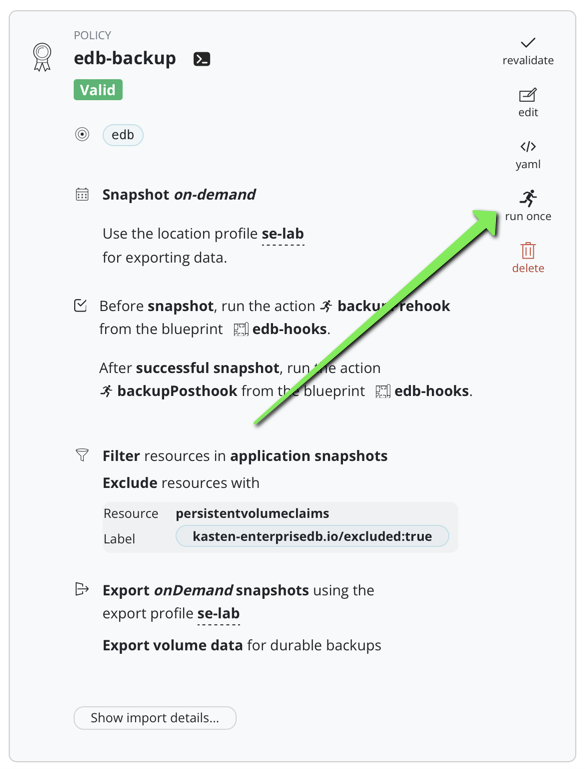
Create a backup policy with the exclude filters and the hooks
Create a Kasten policy for the edb namespace: set up a location profile for export and kanister actions.
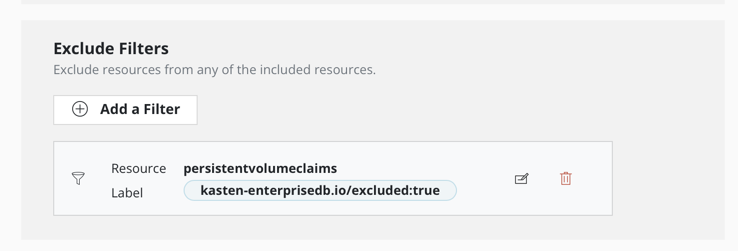
Add the exlude filters :
kasten-enterprisedb.io/excluded:true
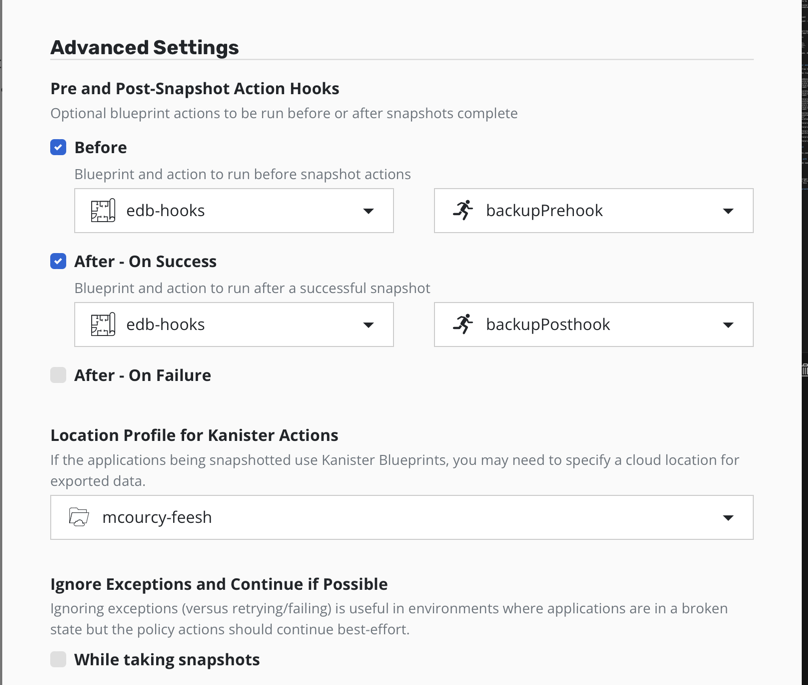
Add the hooks :
Launch a backup
Launch a backup, this creates 2 restorepoints a local and a remote.
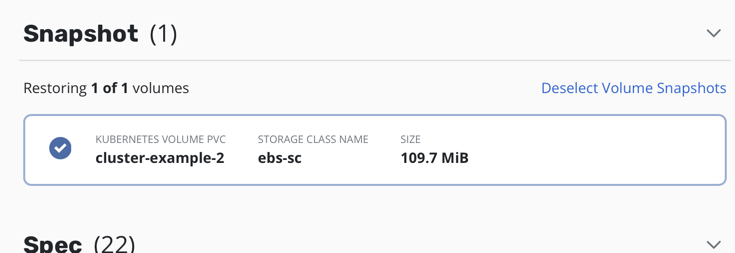
When checking the kasten restore point you can notice that only one PVC has been backed up (the one that was “fenced”).
Let’s test a restore
Delete the namespace edb
kubectl delete ns edb
Restore
Because you deleted the namespace all the volumesnaphot are gone hence you need to restore from the external location profile.
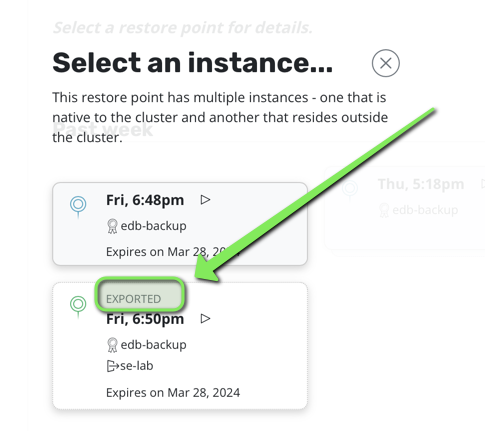
Just click restore and wait for the EDB cluster to restart.
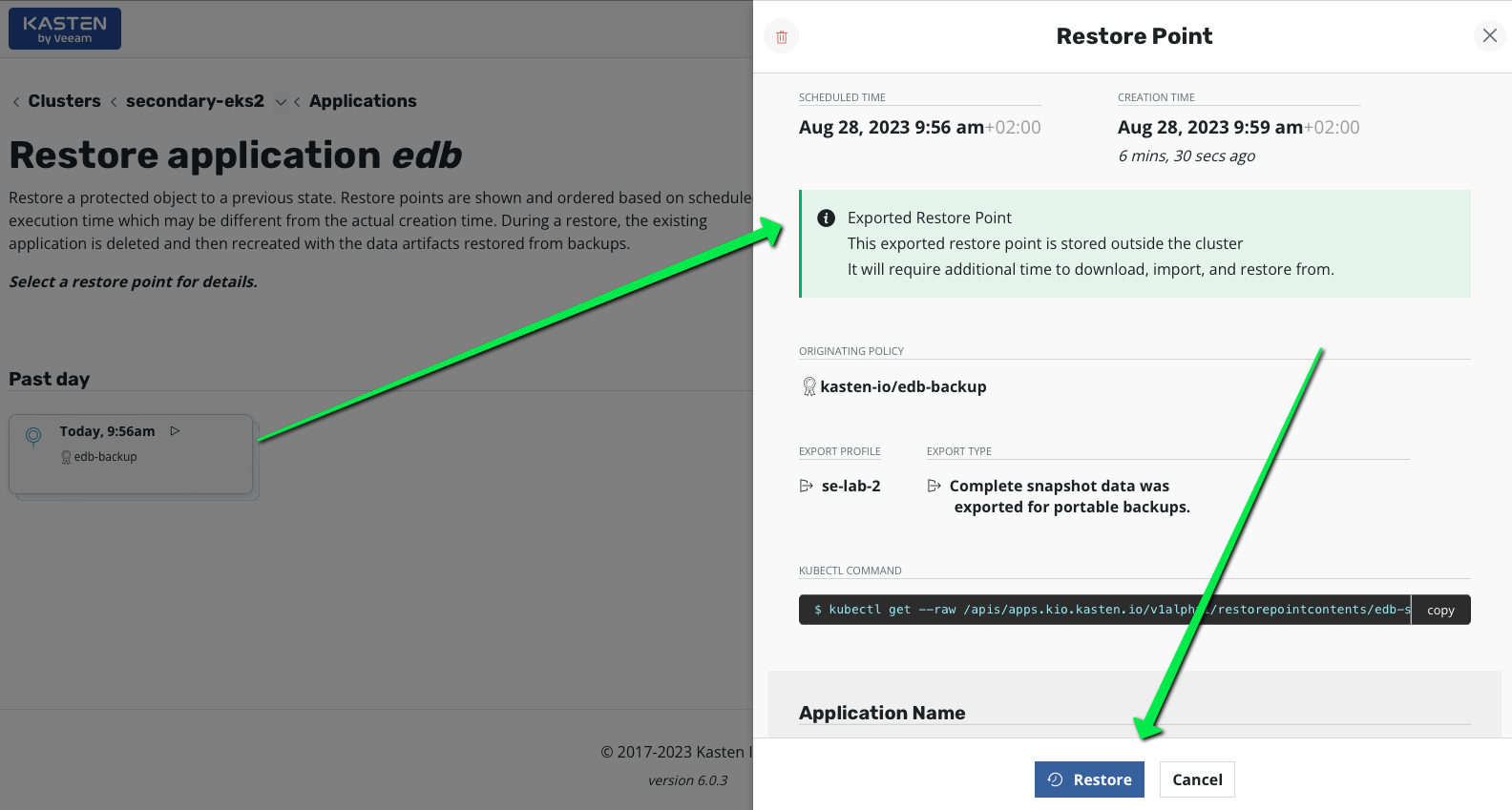
You should see pod cluster-example-2 immediatly starting (without initialization of the database) and the cluster-example-3 and cluster-example-4 joining.
kubectl get po -n edb -w
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
cert-test-5dcf5cb6b8-fhf4m 1/1 Running 0 3s
cluster-example-2 0/1 Init:0/1 0 1s
cluster-example-2 0/1 PodInitializing 0 3s
cluster-example-2 0/1 Running 0 4s
cluster-example-2 1/1 Running 0 5s
cluster-example-2 1/1 Running 0 5s
cluster-example-3-join-vm6d9 0/1 Pending 0 0s
cluster-example-3-join-vm6d9 0/1 Pending 0 5s
cluster-example-3-join-vm6d9 0/1 Init:0/1 0 5s
cluster-example-3-join-vm6d9 0/1 PodInitializing 0 10s
cluster-example-3-join-vm6d9 1/1 Running 0 11s
cluster-example-3-join-vm6d9 0/1 Completed 0 13s
cluster-example-3-join-vm6d9 0/1 Completed 0 15s
cluster-example-3-join-vm6d9 0/1 Completed 0 16s
cluster-example-3 0/1 Pending 0 0s
cluster-example-3 0/1 Pending 0 0s
cluster-example-3 0/1 Init:0/1 0 0s
cluster-example-3 0/1 PodInitializing 0 4s
cluster-example-3 0/1 Running 0 5s
cluster-example-3 0/1 Running 0 5s
cluster-example-3 1/1 Running 0 6s
cluster-example-4-join-rtpxf 0/1 Pending 0 0s
cluster-example-4-join-rtpxf 0/1 Pending 0 5s
cluster-example-4-join-rtpxf 0/1 Init:0/1 0 5s
cluster-example-4-join-rtpxf 0/1 PodInitializing 0 9s
cluster-example-4-join-rtpxf 0/1 Completed 0 10s
cluster-example-4-join-rtpxf 0/1 Completed 0 12s
cluster-example-4-join-rtpxf 0/1 Completed 0 13s
cluster-example-4 0/1 Pending 0 0s
cluster-example-4 0/1 Pending 0 0s
cluster-example-4 0/1 Init:0/1 0 0s
cluster-example-4 0/1 PodInitializing 0 6s
cluster-example-4 0/1 Running 0 7s
cluster-example-4 0/1 Running 0 7s
cluster-example-4 1/1 Running 0 8s
cluster-example-4-join-rtpxf 0/1 Terminating 0 21s
cluster-example-3-join-vm6d9 0/1 Terminating 0 43s
cluster-example-4-join-rtpxf 0/1 Terminating 0 21s
cluster-example-3-join-vm6d9 0/1 Terminating 0 43s
cluster-example-3 1/1 Running 0 28s
cluster-example-2 1/1 Running 0 50s
cluster-example-4 1/1 Running 0 9s
Check your data are back.
As Kasten restores everything that was backed up by default it has also restored the client. Connect to the client and check the data.
kubectl exec -it deploy/cert-test -- bash
psql " $DATABASE_URL "
\c app
select * from links;
\q
exit
You should see your data back
app=> select * from links;
id | url | name | description | last_update
----+-------------------+--------+----------------------+-------------
1 | https://kasten.io | Kasten | Backup on kubernetes | 2024-03-25
Conclusion
This partnership between Kasten and EDB is really a great opportunity for devops that were looking for a postgres managed database without being tied to a specific cloud provider. Now your database is fully managed and you can migrate it seamlessly in your different Kubernetes clusters.